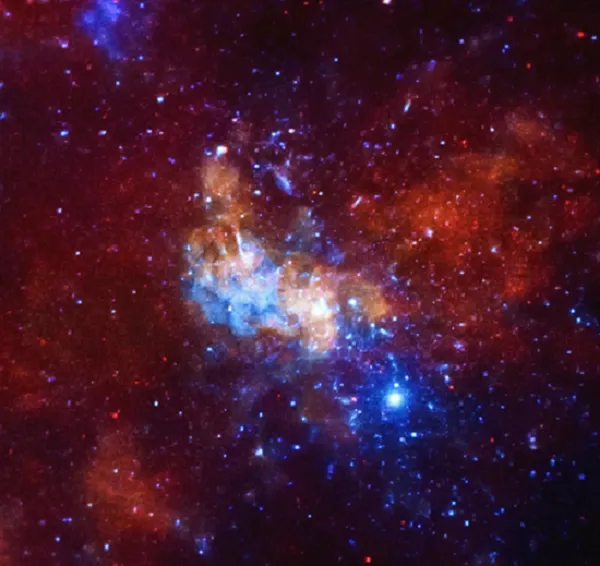
The gravity of a black hole is so strong that not even light can escape. When mass is compressed into a small volume, gravity increases dramatically. A fading star may experience this. Black holes are invisible because no light can escape them. None of us can see them. To locate black holes, specialized space telescopes can be used. Stars near black holes exhibit peculiar behavior, which can be observed by using the specialized equipment. The concept of a gigantic and dense extraterrestrial object that would prevent light from escaping has been around for ages. Einstein's general theory of relativity famously predicted black holes by demonstrating that the Centre of a big star that has died is compact and dense. The equations demonstrated that a black hole is created if the core's mass is greater than nearly three times the mass of the Sun.
The first is a black hole of stellar mass. These are the remains of massive stars. When a star with more than five times the mass of our sun bursts as a supernova, gravity compresses its core abruptly and violently. Depending on the mass of the star, the collapse may come to a standstill and form a neutron star. However, if the core's mass is adequate, the collapse will continue, becoming a black hole. Stellar-mass black holes have masses ranging from around five times the mass of our sun to about 60 times the mass of our sun. Their diameter ranges between 10 and 30 miles (16 and 48 kilometers). In 2021, scientists revealed the finding of an intermediate-mass black hole. This form of black hole spans the gap between stellar-mass black holes and supermassive black holes, which lurk at the heart of galaxies. The recently discovered "goldilocks" black hole contains 55,000 suns in mass. The researchers discovered the intermediary black hole by detecting something far behind it: gamma ray burst emissions. Scientists discovered the intermediate-mass black hole by gravitational lensing of the burst's light.

The supermassive black hole is the third type of black hole. These can be billions of suns in size. Most galaxies, astronomers believe, have supermassive black holes at their centers. Sagittarius A*, the one at the center of our own Milky Way galaxy, has 4 million times the mass of our sun and is 37 million miles in circumference.
Another example of a supermassive black hole can be found at the heart of the quasar TON 618. Its center black hole is predicted to be 66 billion solar masses in size. A micro black hole is another type of black hole that may exist. These would be far smaller than a stellar-mass black hole.
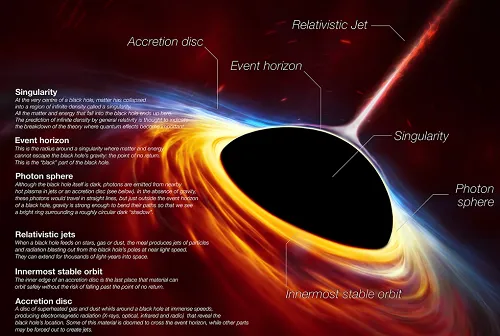
The event horizon of a black hole is its border. It's not a physical advantage. It is just a point in space beyond which it is impossible to escape the gravity of a black hole. Anything falling into the black hole that passes the event horizon will never be able to leave the black hole again.

The researchers gained a clearer look at the event horizon of M87 by revealing it in polarized light, which is also known as the "point of no return" since it is the point at which no matter can move closer to the black hole without being pulled in. The sun will never become a black hole. The sun is not a powerful enough star to become a black hole. NASA is learning more about black holes by sending satellites and telescopes into space.