Bitcoin uses blockchain technology to facilitate its decentralized, peer-to-peer transactions. The Bitcoin blockchain is a decentralized and open database. Decentralized and operating independently of central banks or other intermediaries, bitcoin was originally presented in 2008. Bitcoin is a digital currency that may be transferred between users using the blockchain-recorded peer-to-peer Bitcoin network. Bitcoin's high degree of openness is a major benefit.
Block. A block is a collection of Bitcoin transactions that occurred at around the same time. Transactions are confirmed by "miners," who receive newly produced Bitcoin in exchange for their services.
Money in Bitcoins. Bitcoins may be divided up to eight digits of precision. One thousand millibitcoins (mBTC) is equal to one Bitcoin. A satoshi (sat) is equal to one hundred millionth of a Bitcoin. One Bitcoin (BTC) is equal to one million BTC, and the smallest fraction of a Bitcoin is 0.000000001 BTC. After its first distribution as free software in 2009, Bitcoin wasn't used until Nakamoto mined the first block of the blockchain. The first fifty Bitcoins were stored in this block, which is now known as the Genesis Block.
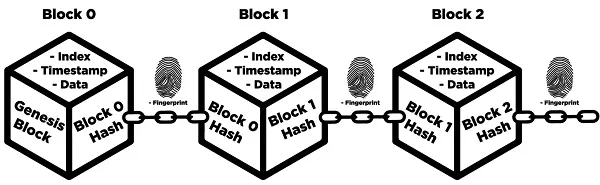
There are currently little more than 18,800,000 Bitcoins in circulation. It is through "Bitcoin mining" that new Bitcoins are generated and "block rewards" are given out. Blockchain, Each exchange creates a new, solid link in the chain. Bitcoin's existence and utility are made possible by this open, public chain. The term "blockchain" originates from the fact that each set of recorded transactions is inextricably linked to its predecessors.
Mining, Each block is the result of time-consuming and expensive computer calculations performed independently by a number of people. To ensure the blockchain remains reliable, complete, and unchangeable, block hash and mining activities involve a record-keeping service. Hashes are used to verify the supply of Bitcoin and to fairly compensate miners for their efforts. As part of the bitcoin mining process, the decentralized network verifies all Bitcoin transactions. Complex algorithms are solved by multiple computers in a race against the clock. Bitcoins are given as payment to the machine that solves the algorithm and verifies the block's worth of Bitcoin transactions on the blockchain.

The blockchain address A string of 25–34 alphanumeric characters. This is the information provided to other parties in order for them to know where to transfer the currency. They are referred to be pseudonymous because, while the blockchain itself is public, the address conceals personally identifiable information. To protect anonymity, cryptocurrency exchanges may be compelled by law to collect personally identifiable information, but each transaction can be connected with a separate Bitcoin address. Wallet, Any individual or entity intending to swap Bitcoin (rather than storing it on an exchange in someone else's custody) must first build a digital collection of the credentials required to transact bitcoin, known as a wallet.

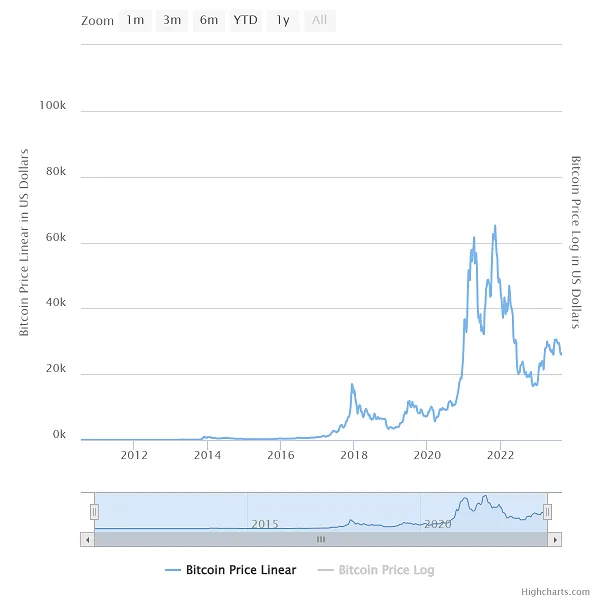
Nakamoto designed the method to ensure that no more than 21 million bitcoins would ever be created. Over 18 million have been extracted thus far. The current rate of mining indicates that 21 million bitcoins will be mined by the year 2140 at the latest. Their worth keeps rising, despite the fact that prices are always changing. A bitcoin was valued less than one penny in October of 2009. The current value of a single bitcoin is over $35,000 USD. It is widely believed that Bitcoin's anonymous developer used the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. There has been much conjecture about who created Bitcoin, but no one knows for sure. Bitcoin is the first and most widely used cryptocurrency. Many people have been experimenting with concepts similar to Bitcoin's blockchain for a long time, and cryptography has been around for a long time. When a white paper explaining a decentralized digital currency system was released in 2008 under the alias Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin was officially introduced to the world. Bitcoin is a system that uses this.
Bitcoin's blockchain network creates and hashes blocks using a mechanism called proof-of-work. Using proof-of-work for mining requires a network computer to go through a difficult mathematical issue. If one computer (a "node" in the network) finds a solution, the others must agree that it is correct. In that case, the transaction has been successfully confirmed and the miner whose node solved it has been awarded Bitcoins. Bitcoin's Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism is another essential component that permits decentralization. To add new blocks to the blockchain, nodes participating in Proof-of-Work (PoW) systems must solve difficult mathematical puzzles. Mining is the procedure that ensures no single node has monopoly power over the network. Retail, mining, travel, healthcare, education, agriculture, and even the entertainment business are just a few that will be impacted by blockchain technology. Perhaps most significantly, the trend toward decentralized finance, which employs permissioned blockchains to manage complicated financial use cases, suggests that the financial services industry may be the one to feel the greatest impact. It's also likely that governments will keep supporting blockchain technology.