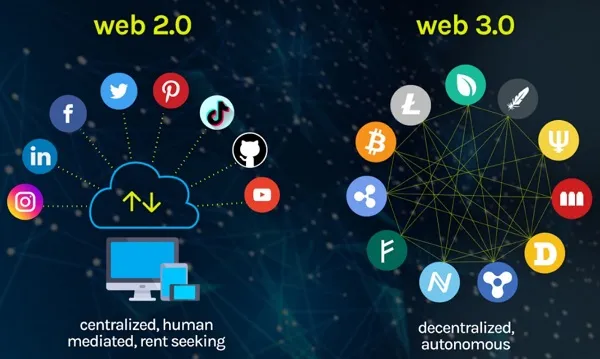
There are now just two versions of the internet available. Web 1.0, also known as the read-only web, was in existence from the advent of the internet in 1989 until the early 2000s. The site was created to disseminate data, but it did not encourage participation from site visitors. You might either publish your own web pages or visit the pages of others. The discussion is over. There was no means of contact besides email. A server retained all the data, and only a computer could retrieve it. Web 2.0, often known as the "Read-Write Web" is the second iteration of the World Wide Web. The current standard was adopted around the year 2004. People can now respond to anything they find online in various ways, including comment areas, social media, and more. In Web 2.0, data is stored in the cloud and can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, not only PCs and Macs. Google, Amazon, Facebook, and Twitter are just a few of the platforms that have evolved to simplify online communication and commerce. We, the users, contribute to the success of these platforms but have little to show for it because ownership is concentrated in the hands of a few firms. Therefore, solutions based on Web 3.0 are necessary.
Individuals in the Web3 world are the gatekeepers of their own data, and they use a unified profile for everything from social networking to email to online commerce, with each transaction recorded in the public ledger known as the blockchain. It's a system in which a network of computers stores information that can be accessed by anybody conducting a search. Users act as a group rather than a business in charge. "Tokens" are awarded to those who take part. Tokens can be used to cast votes and even gain value over time. Web3's fundamental goal is to make information sharing more open and decentralized so that everyone may benefit from online communities. Distributed computing envisions a future in which data is freely exchanged and kept in many locations, rather than centralized databases like Google's. DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) will manage everything collectively. Web3 can easily solve the privacy and data control problems that plague many users and businesses today. Our favorite internet destinations, including the servers on which they run, are typically owned by corporations that in turn must comply with government restrictions. This is because this was the least complicated method of constructing a network: having a third party pay to set up servers with the programs that end users will need access to over the internet.
Blockchain, the underlying technology, is a "distributed ledger" a database hosted by a network of computers rather than a single server that provides users with an immutable and transparent means to store information. Information is located on many machines or servers. The information in a file is invalid if a single copy does not exactly match all the other copies. This provides an extra layer of security by making it such that only the person who controls the data, or the entire dispersed network, may make changes to it. To produce "digital deed" ownership records of unique digital things or nonfungible tokens is one example of a new use case for blockchain technology. In 2022, the market for NFTs blew out. DeFi (Decentralized Finance) advocates for the elimination of traditional financial institutions. Blockchain technology is being used to alter traditional data management practices. A blockchain-based web could theoretically break down existing information and financial monopolies, as well as transform the very nature of networks and corporations.
In the past, the "web 3.0" label was commonly used to refer to what is now called the "Semantic Web" Sir Tim Berners-Lee, also known as the "father of the internet" proposed this idea for a machine-to-machine internet. The terms "open," "trustless," and "permissionless" are frequently used to describe the characteristics of the web3's underlying technology architecture. To interact and transact with no requirement for a third party who can be trusted is the definition of a trustless system. Web3 trustless transactions include transmitting Bitcoin straight to another individual, without going through a centralized server or online exchange. The blockchain technology and encryption make it nearly impossible for a third party to interfere with a transaction in progress. A third party (such as a service provider or government) is not required for a transaction or interaction to take place.

Users of Web3 are more than just passive viewers. Instead of being asked to trade personal data for access to platforms, they are owners of the community and earn incentives for involvement. Data stored on the network and access to the service are both available to everyone who uses the network. In Web3, your personal information is linked to your virtual wallet. The public can see what you do online, but you can hide your true identity. The blockchain's incorporation of AI, ML, and smart contracts expedites the dissemination of high-quality information to consumers. No one is prevented from joining Web3 or taking part in its activities. Instead of using the antiquated banking and payment processing infrastructure, bitcoin is used for online spending and transfer of funds. Instead of relying on neutral third parties, it operates on the basis of economic incentives and procedures.
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs):
Web 3.0 coinage, a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is a corporation, association, or other entity whose members are obligated to follow the laws and regulations written into its blockchain. All product prices and information about who is eligible for distributions in a DAO-based store, for instance, would be stored on a distributed ledger. DAO shareholders would have a say in setting pricing and allocating funds. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) enable coordinated, decentralized platform ownership and governance. As a technical matter, DAOs are consensus-based smart contracts that manage distributed consensus over a shared asset supply (tokens). Token holders have a say in allocating scarce resources, and the programming follows their wishes to the letter. However, no one could alter the regulations without express approval. It was also impossible for the owners of the underlying hardware, such as servers or the buildings housing the earnings, to tamper with the system in any manner.
Some disadvantages of Web3:
Blockchain systems are quite costly to run and consume a lot of resources. Since this is the foundation upon which Web3 is built, it remains true. To get the most out of Web3 platforms and apps, users may need to upgrade their hardware. There may not be enough storage space or processing power in an older gadget. There is a pressing need for more scalable computing resources to support the widespread adoption of blockchain technology for use in peer-to-peer transaction processing. Since the absence of scale raises costs and limits who can take part, centralization is inevitable. Due to the virtual nature of DAOs, good data governance is essential for reasons of safety, accessibility, collaboration, and more. DAOs rely on digital data for their infrastructure and operation. One of the first things to consider when developing governance guidelines is how to ensure that this data is properly managed with a specialized tool. Web3 has many potential upsides, but its existing ecosystem still has a lot of work to do before it can truly thrive.
In web3, AI will be essential. This is because many web3 applications will require machine-to-machine communication and decision-making. In the context of web3, the term "Metaverse" refers to the next generation of the internet's front end, or the graphical user interface (GUI) through which we access the internet and engage in activities like browsing, messaging, and data manipulation. Even though Web 3.0 has a lot of potential, don't expect a dramatic shift overnight. The current internet will gradually transition into the new one over time.