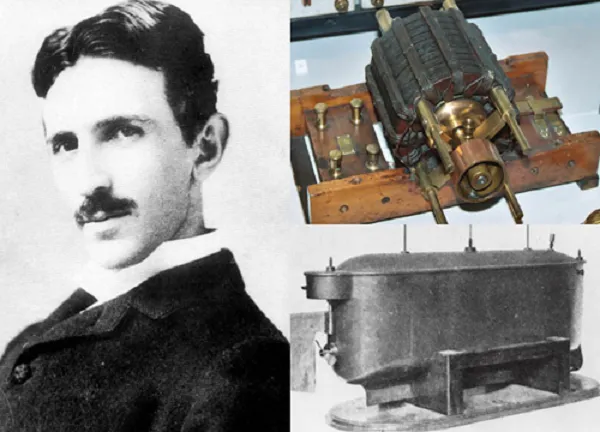
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, in Austro-Hungarian Smiljan, Croatia. According to Tesla's birth story, he was born on a summer night in 1856 during a lightning storm, prompting the midwife to prophesy, "He will be a child of the storm," and his mother to respond, "No, of the light."* Teachers suspected Tesla of cheating because of his extraordinary aptitude at solving mathematical problems. He was sick when he was a teenager, and he only got better after his father gave up on his dream of making Nikola a priest and let him study engineering instead. His mother ran the property and his father was a Serbian Orthodox priest. Tesla's brother Daniel died in a riding accident in 1863. The death surprised 7-year-old Tesla, who saw visions—the earliest indicators of his lifelong mental disorder. He had a fantastic imagination, creativity, and even a poetic touch as he got older.

In 1884, he moved to the United States to work for Thomas Edison after a rocky scholastic career in Europe, where he had worked as a telegraph drafter and electrician. If you've ever tried to picture yourself living without a TV remote, you have Nikola Tesla to thank. The remote control, neon and fluorescent lights, wireless transmission, computers, smartphones, laser beams, x-rays, robotics, and, of course, alternating current, the basis of our modern electrical system are just a few examples of the hundreds of technologies that Tesla invented, predicted, or contributed to development of.

Tesla was born with an inventive spirit. Tesla once reflected, "My mother was an inventor of the first order and would, I believe, have achieved great things had she not been so remote from modern life and its multi fold opportunities." She spun her own thread and fashioned a wide variety of weaving implements and textiles. He said that he had been successful because of his parents' influence. The Tesla coil, immortalized in the tower at the Tesla Science Center in Wardenclyffe in Shoreham, New York, is perhaps the most recognizable symbol of Tesla's work. Here, Tesla built a tower upon which he placed his notorious coils, which, using alternating current, fired electric sparks across the air.
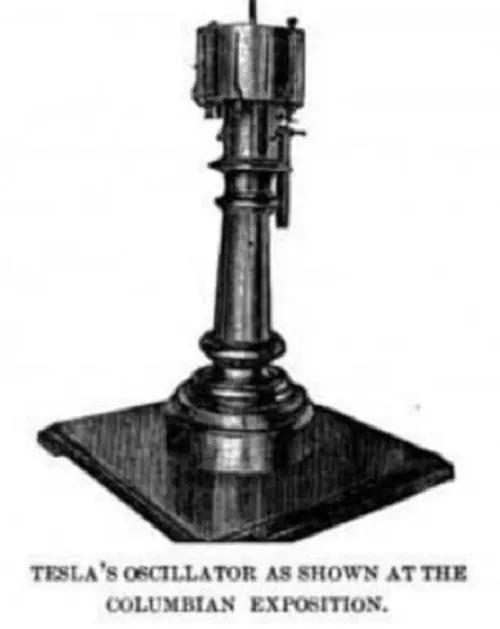

There are still reminders of Tesla's 60-year tenure in New York City. Because of its proximity to Tesla's laboratory at 8 West 40th Street, where he worked in 1900 while building his now-famous Tesla Tower on Long Island, the intersection of 40th Street and 6th Avenue in midtown Manhattan has been officially named "Nikola Tesla Corner" with its own street sign. Tesla built the first hydroelectric power station near Niagara Falls, New York, to capture the power of the waterfalls he had admired since childhood. Using combustion to turn disks, Tesla created a piston engine to power automobiles. X-rays can also be referred to as the Shadowgraph. Tesla improved upon preexisting neon light technology to create the neon lamp (or sign). Bars, casinos, hotels, and other signage along the highway still use neon signs to this day.

Tesla's induction motor powers vacuums, hairdryers, and power tools with electromagnets. Tesla is regularly included in science fiction movies and TV shows due of his far-out theories. At Graz, he discovered the Gramme dynamo, which could generate electricity and run as a motor when reversed. Tesla designed his first radio-controlled boat, the Teleautomaton. Tesla's biggest achievement is alternating current. Although not the originator of AC electricity, he made it widely available. Tesla invented a remote-controlled teleautomatic watercraft in 1898. Tesla demonstrated it to Madison Square Garden crowds after skepticism. He believed he had received signals from another planet in his Colorado lab, but other scientific journals mocked him.

Incredibly, Tesla lived. Tesla believed he had his most profound insights while working alone. The Serbian-born inventor was granted over 300 patents during his lifetime. Tragically, Tesla passed away on January 7, 1943, in his bedroom. To finally give credit where credit is due, the Supreme Court of the United States invalidated four of Marconi's most important patents later that year.

His upgraded version of the AC system, which he championed, is now the gold standard for power transmission around the world.